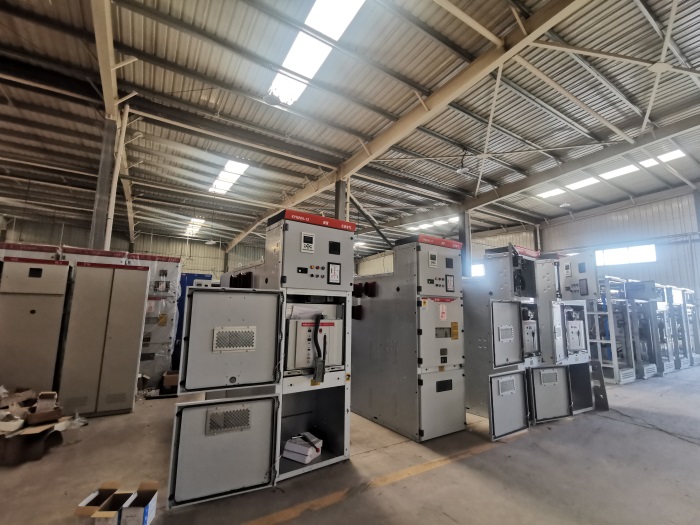
high-voltage outgoing switchgear
Product description
 **I. Definition and Functions**
**I. Definition and Functions**
1. **Definition**
- The high-voltage outgoing cabinet is a type of high-voltage switchgear. In the high-voltage power distribution system, it is mainly used to connect high-voltage busbars and outgoing cables and is a key equipment for distributing high-voltage electric energy from substations or power distribution rooms to various electrical equipment or lower-level substations.
2. **Functions**
- **Power distribution**
- Obtain electric energy from high-voltage busbars and distribute it to different load lines or lower-level substations. For example, in the power supply system of a large factory, the outgoing cabinet distributes the high voltage from the main step-down substation to the transformers or large electrical equipment in each workshop.
- **Protection function**
- Equipped with various protection devices to protect the safe operation of the outgoing circuit. Common protection functions include overcurrent protection, instantaneous trip protection, zero-sequence protection, etc. Overcurrent protection can automatically cut off the circuit when the outgoing current exceeds a certain multiple of the rated current to prevent equipment damage or fire hazards caused by line overload; instantaneous trip protection is for serious faults such as line short circuits and can act quickly to cut off the faulty circuit quickly and reduce the impact of faults on the entire system; zero-sequence protection is mainly used to detect grounding faults and acts in time when a single-phase grounding fault occurs in the outgoing circuit.
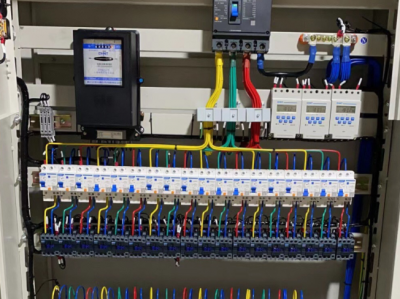
- **Measurement and monitoring**
- Measuring instruments such as ammeters and voltmeters are usually installed inside for real-time measurement of electrical parameters such as current and voltage of the outgoing circuit. At the same time, intelligent monitoring devices can also be equipped to transmit measurement data to the monitoring system so that operation and maintenance personnel can remotely monitor the operating status of the outgoing circuit and discover abnormal situations in time, such as voltage fluctuations and current imbalance.
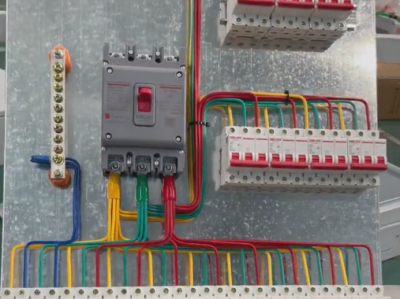
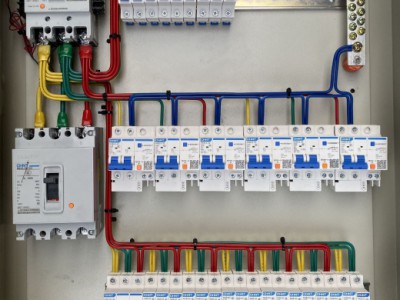
**II. Structural Composition**
1. **Cabinet body** - Generally, a metal-enclosed structure is adopted, such as a cabinet body made of steel plates, which has good mechanical strength and protection performance. The protection level of the cabinet body varies according to different use environments. Common protection levels such as IP3X and IP4X can prevent foreign objects from intruding into the cabinet body and protect internal electrical components from dust, small animals, and other intrusions.
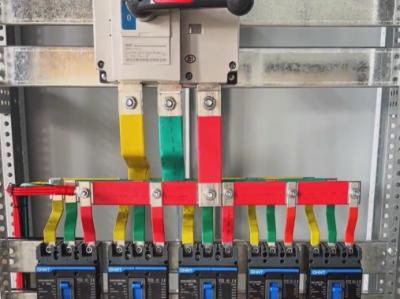
2. **Circuit breaker**
- It is one of the core components of the high-voltage outgoing cabinet. Commonly used high-voltage circuit breakers include vacuum circuit breakers and SF6 circuit breakers. Vacuum circuit breakers use vacuum as the arc-extinguishing medium and have advantages such as good arc-extinguishing performance, long service life, and simple maintenance; SF6 circuit breakers use sulfur hexafluoride gas as the arc-extinguishing and insulating medium and have strong current-breaking capacity and are suitable for high-voltage and large-capacity outgoing circuits. The main function of the circuit breaker is to reliably connect and cut off the circuit under normal and fault conditions.
3. **Disconnector**
- The disconnector is used to isolate the power source during maintenance to ensure the safety of maintenance personnel. It cannot be operated under load. The operation sequence is generally to operate the disconnector after the circuit breaker is disconnected. The disconnector has an obvious disconnection point, which is convenient for operation and maintenance personnel to intuitively confirm whether the circuit has been cut off.
4. **Current transformer and voltage transformer**
- The current transformer (CT) is used to transform large currents into small currents for use by measuring and protection devices. For example, transform the large current of several hundred amperes or even thousands of amperes in the outgoing circuit into a standard small current of 5A or 1A and supply it to equipment such as ammeters and protection relays. The voltage transformer (VT) transforms high voltage into low voltage. For example, transform the high voltage of 10kV into a low voltage of 100V for measurement and metering use by voltmeters and watt-hour meters.
5. **Protection relay**
- According to different protection functions, there are overcurrent relays, instantaneous trip relays, zero-sequence relays, etc. These relays can detect changes in electrical quantities in the circuit. When the electrical quantity exceeds the set value, they automatically send signals to trip the circuit breaker, thereby realizing protection of the outgoing circuit.
6. **Busbar and wiring terminals**
- The busbar is a conductor for collecting and distributing high-voltage electric energy. In the outgoing cabinet, the busbar introduces high voltage into the cabinet and is connected to electrical components such as circuit breakers and disconnectors through wiring terminals to realize the transmission and distribution of electric energy. Wiring terminals are used to connect different electrical equipment to ensure the reliability of electrical connections.
**III. Operation and Maintenance**
1. **Operation points**
- **Power transmission operation**
- First, check that the appearance of each electrical component of the outgoing cabinet is normal, the instrument indication is normal, and the protection device is correctly put into operation. Then operate in the order of closing the disconnector first and then closing the circuit breaker. When operating the disconnector, ensure that the circuit breaker is in the off state to prevent pulling and closing the disconnector under load.
- **Power outage operation**
- The order is opposite to that of power transmission operation. First, disconnect the circuit breaker and then open the disconnector. During the operation, pay attention to observing the instrument indication and the action of the protection device to ensure safe and reliable operation.
2. **Maintenance requirements**
- **Regular inspection**
- Operation and maintenance personnel need to regularly inspect the high-voltage outgoing cabinet, check whether the cabinet body has damage, corrosion, and other conditions; check whether the operating mechanisms of circuit breakers and disconnectors are flexible and whether the connection parts are loose; check whether the operation of instruments and protection devices is normal and whether there are alarm signals.
- **Preventive test**
- Conduct preventive tests on the outgoing cabinet according to the specified cycle, such as conducting closing and opening time and synchronism tests on circuit breakers and conducting insulation resistance and withstand voltage tests on insulation parts. These tests can detect potential problems of the equipment in advance and ensure the safe operation of the outgoing cabinet.
- **Component replacement and maintenance**
- When damaged electrical components are found, such as severely worn circuit breaker contacts and relay failures, they should be replaced or repaired in time. When replacing components, products that meet the specification requirements should be selected and installed and debugged in strict accordance with operating procedures.