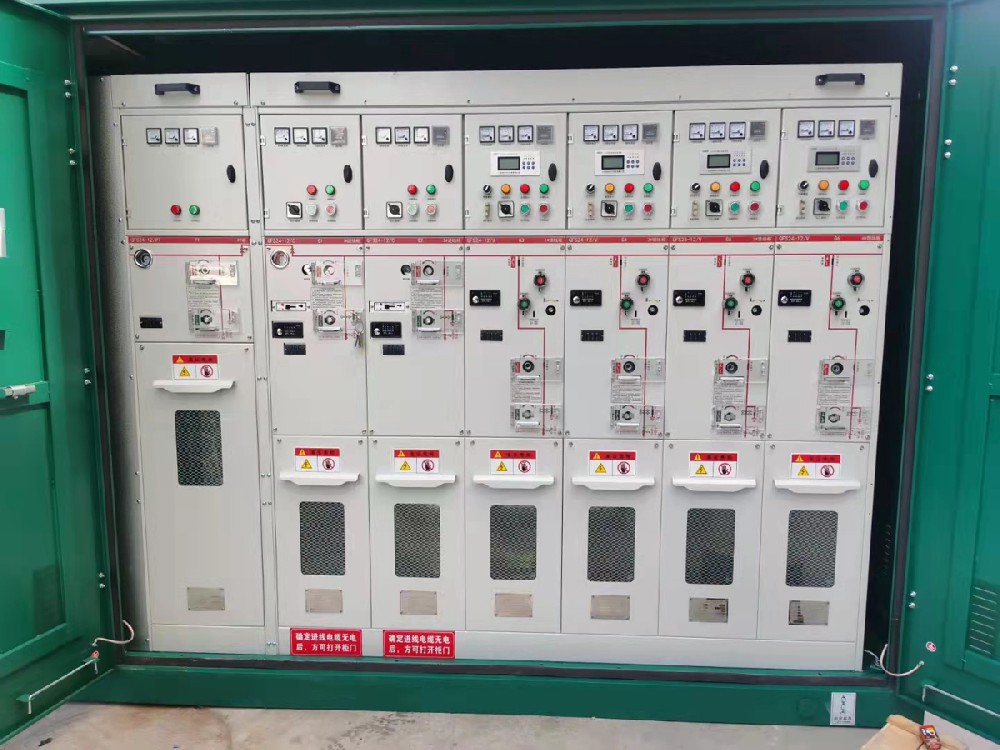
High voltage switchgear
Product description
 *I. Definition and Functions**
*I. Definition and Functions**
1. **Definition**
- High-voltage switchgear is an electrical equipment that plays a role in on-off, control, or protection in power generation, transmission, distribution, electric energy conversion, and consumption in power systems. Its rated voltage is 3kV or above. It is mainly used to receive and distribute electric energy and control, protect, and monitor circuits.
2. **Functions**
- **Power distribution**
- Distribute electric energy from high-voltage transmission lines or substations to different branches or loads. For example, in the high-voltage power distribution room of a large factory, distribute the high-voltage electricity of the total incoming line to the high-voltage electrical equipment in each workshop.
- **Circuit control**
- Realize the on-off control of high-voltage circuits through components such as circuit breakers and disconnectors. For example, in a substation, control the power transmission and outage operations of different lines.
- **Protection function**
- It has multiple protection functions, such as short-circuit protection, overcurrent protection, overvoltage protection, and undervoltage protection. When a short circuit occurs in the circuit, the circuit breaker will quickly cut off the circuit to prevent the fault from expanding and protect the safety of equipment and personnel; overcurrent protection can act when the current exceeds the rated value to avoid damage to the equipment due to long-term overcurrent; overvoltage and undervoltage protection can protect the equipment when the voltage is abnormal to ensure its normal operation.
- **Monitoring function**
- Use equipment such as voltage transformers, current transformers, arresters, and various monitoring instruments to monitor parameters such as voltage, current, and power factor in high-voltage circuits. Operation and maintenance personnel can promptly discover circuit faults or abnormal operation conditions according to the monitoring data.
**II. Structural Composition**
1. **Cabinet body**
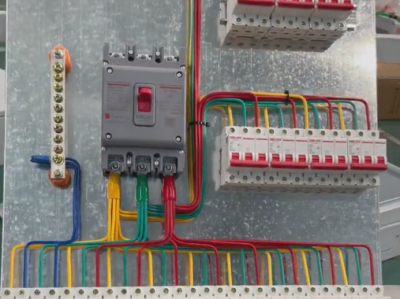
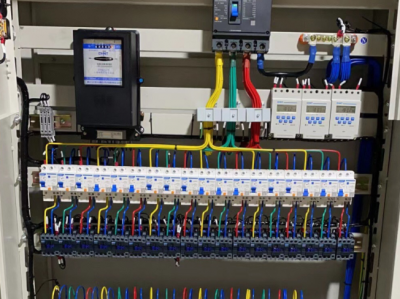
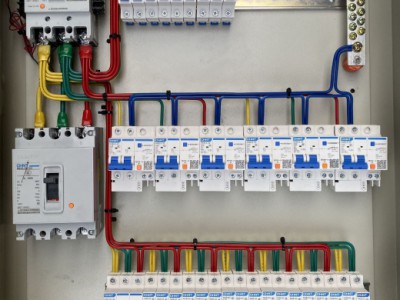
- The cabinet body is the shell of high-voltage switchgear. Generally, metal materials such as steel plates are used, which have sufficient strength and rigidity to protect the internal equipment and personnel safety. The cabinet structure design should consider factors such as insulation performance, protection level, and heat dissipation. Protection levels such as IP30 and IP40. A higher protection level can prevent dust, small animals, etc. from entering the cabinet and avoid short-circuit and other faults. The inside of the cabinet is usually divided into different compartments, such as busbar compartment, circuit breaker compartment, cable compartment, etc. Each compartment is isolated from each other to improve safety.
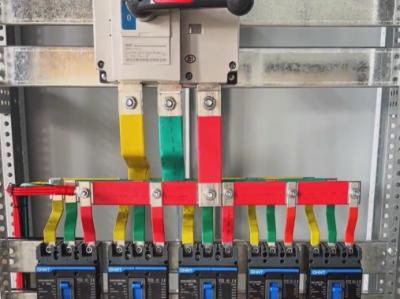
2. **Electrical components**
- **Circuit breaker**
- It is one of the core components of high-voltage switchgear and is used to cut off and connect circuits. It can act quickly in case of a fault and cut off the current. Common ones are oil-minimum circuit breakers, vacuum circuit breakers, SF6 circuit breakers, etc. Vacuum circuit breakers have the advantages of good arc extinguishing performance, long service life, and simple maintenance; SF6 circuit breakers have the characteristics of strong arc extinguishing ability and large breaking capacity and are suitable for high-voltage and large-capacity circuits.
- **Disconnector**
- It is mainly used to isolate the power supply to ensure the safety of maintenance. After the circuit is disconnected, the disconnector isolates the equipment to be maintained from the live part to form an obvious disconnection point to prevent electric shock accidents caused by misoperation. The disconnector cannot be operated under load. The operation sequence must be to disconnect the circuit breaker first and then operate the disconnector.
- **Current transformer and voltage transformer**
- The current transformer converts a large current into a small current for use by measurement and protection devices. The voltage transformer converts high voltage into low voltage for use by measurement, metering, and protection equipment. They are important elements for realizing the measurement of high-voltage circuit parameters and protection functions.
- **Arrester**
- It is used to protect electrical equipment from damage caused by lightning overvoltage and switching overvoltage. When lightning overvoltage or switching overvoltage acts on the circuit, the arrester will conduct first and limit the overvoltage within a certain range, thereby protecting other equipment.
- **Earthing switch** - During maintenance, the earthing switch is used to ground the equipment and release the possible residual charges on the equipment to ensure the safety of maintenance personnel. The operation of the earthing switch has strict interlocking requirements to prevent misoperation.
**III. Common Types**
1. **Armored withdrawable switchgear (center-mounted cabinet)**
- The circuit breaker is installed on a withdrawable center-mounted trolley. The trolley can be conveniently pushed in or pulled out of the cabinet for maintenance or replacement. This kind of switchgear has high safety and reliability and is widely used in substations and power distribution rooms with voltage levels of 10 - 35kV. Its compartments such as the busbar compartment and circuit breaker compartment are reasonably arranged and have good protection performance.
2. **Fixed switchgear**
- Electrical components are fixedly installed inside the cabinet body, and the structure is relatively simple. This kind of switchgear has a lower cost but is not very convenient for maintenance. It is suitable for places that are more sensitive to cost and have low requirements for maintenance frequency, such as simple power distribution rooms of some small industrial enterprises.
3. **Ring main unit**
- It is mainly used in ring network power supply systems and has the characteristics of a compact structure and small volume. It can realize the connection, distribution, and switching of multiple power sources and improve the reliability of power supply. Ring main units usually use a combination of load switches and fuses to realize the control and protection of circuits and are often used in places such as community power supply and small commercial area power supply in urban distribution networks.
**IV. Installation and Maintenance**
1. **Installation requirements**
- **Environmental requirements**
- It should be installed in a dry, well-ventilated place without violent vibration. Avoid installing it in an environment with high humidity, corrosive gases, or a lot of dust. Otherwise, it may affect the insulation performance and service life of the equipment. If the environmental humidity is high, the insulation material will be damp, reducing the insulation resistance; corrosive gases may corrode metal parts and cause equipment damage.
- **Installation foundation**
- A firm installation foundation is required. Generally, channel steel or concrete foundation is used. When the cabinet body is installed on the foundation, the levelness and verticality must be ensured. The levelness deviation should not exceed the specified value (such as 1‰ - 1.5‰), and the verticality deviation should not exceed the corresponding standard to ensure the stability and normal operation of the equipment.
- **Wiring requirements**
- The wiring of high-voltage cables should comply with safety specifications. The cable connection should be firm and reliable, and insulation treatment should be done well. The cross-sectional area of the cable should be reasonably selected according to factors such as rated current and voltage drop to avoid problems such as heating and excessive voltage loss due to improper cable selection.
2. **Maintenance points**
- **Regular inspection**
- Regularly (such as monthly or quarterly) inspect the high-voltage switchgear to check whether the connections of electrical components are loose, whether the insulation parts are damaged or aged, and whether various instruments are working properly.
- **Insulation test**
- Regularly conduct insulation resistance tests, including phase-to-phase insulation and ground insulation. The insulation resistance value should meet the relevant standard requirements. If a decrease in insulation resistance is found, find the cause in time and take measures to repair it, such as replacing insulation parts or eliminating moisture factors.
- **Component function test**
- Conduct function tests on electrical components such as circuit breakers and disconnectors to check whether their opening and closing actions are normal and whether the operating mechanisms are flexible and reliable. For arresters, regularly detect their operating characteristics to ensure normal operation under overvoltage.