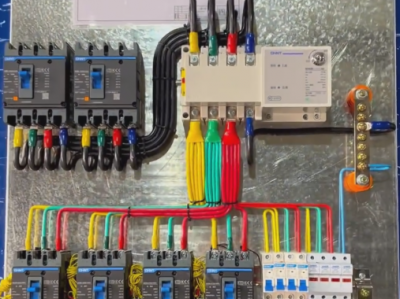
AP Control Cabinet
Product description
 YouTube:https://youtube.com/shorts/YG6RwJmPnE8
YouTube:https://youtube.com/shorts/YG6RwJmPnE8
AP Control Cabinet for Low-Voltage Electrical Applications. The AP control cabinet (power distribution box) is widely used in the field of low-voltage electrical applications. The following is a detailed introduction to it:
### I. Basic Concept The AP control cabinet is mainly used for power distribution and control of low-voltage power equipment. It can receive electrical energy from the superior power distribution equipment and distribute it to various electrical equipment, while providing control and protection functions for these equipment. For example, in a factory workshop, the AP control cabinet can distribute the 380V power supply from the power distribution room to different machine tools, fans and other equipment.
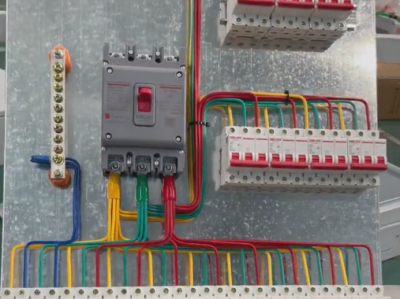
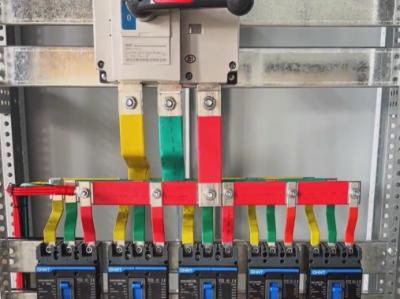
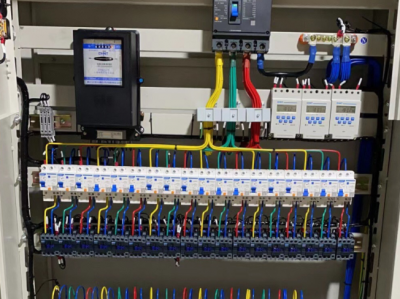
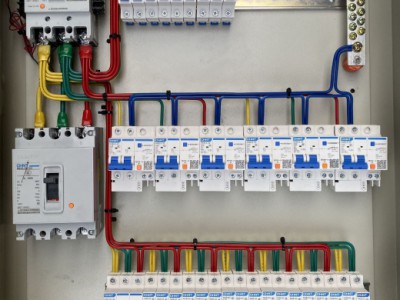
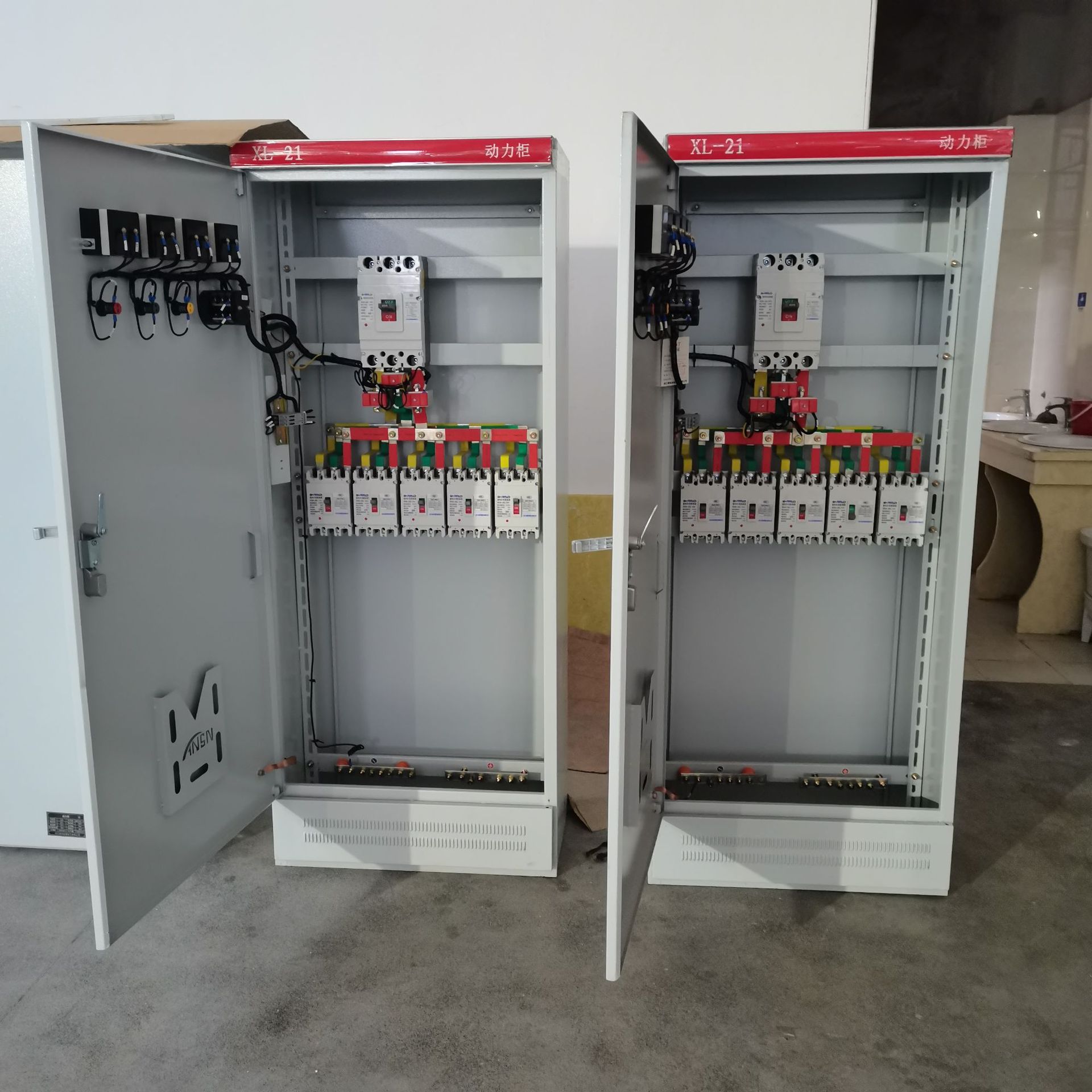
### II. Structural Composition - **Cabinet Body**: - Generally, it is made of metal materials (such as cold-rolled steel plates), having sufficient strength and rigidity to protect the internal electrical components from the interference of the external environment and physical damage. The surface of the cabinet body is usually treated with anti-rust and anti-corrosion processes to extend its service life.
- The design of the cabinet body needs to consider ventilation and heat dissipation. Ventilation openings are usually set on the side or top of the cabinet body, and some will also be equipped with heat dissipation devices such as fans to ensure that the internal electrical components work within the normal temperature range. For example, for some AP control cabinets with relatively high power, good ventilation and heat dissipation can prevent the electrical components from being damaged due to overheating.
- **Electrical Components**:
- **Circuit Breaker**: It is a key protection component in the AP control cabinet. When fault currents such as overload and short circuit occur in the circuit, the circuit breaker can automatically cut off the circuit to protect the downstream electrical equipment. For example, when a motor has a short-circuit fault, the circuit breaker will act quickly to prevent the fault current from causing damage to other equipment and lines.
- **Contactor**: It is used to control the on-off of the circuit. It can realize the start and stop control of equipment such as motors according to control signals (such as those from a PLC or manual buttons). For example, in an automated production line, the contactor is controlled by a PLC to realize the sequential start and stop of motors.
- **Thermal Relay**: It is mainly used for overload protection. It can sense the working current of equipment such as motors. When the current exceeds the set value and lasts for a certain period of time, the thermal relay will act to make the contactor disconnect the circuit, thus protecting the equipment from overload damage.
- **Fuse**: It plays a supplementary role in short-circuit protection in the circuit. When a short-circuit current appears instantaneously, the fuse element will melt and cut off the circuit to prevent the expansion of the fault.
### III. Functional Features
- **Power Distribution Function**:
- The AP control cabinet can distribute the input low-voltage electrical energy to multiple output branches. Each branch can be connected to different electrical equipment. The number and capacity of branches can be flexibly configured according to actual needs. For example, an AP control cabinet can have 4 - 10 output branches, and the rated current of each branch can range from several amperes to several hundred amperes.
- **Control Function**:
- It provides two control methods, namely manual control and automatic control. Manual control is usually achieved by buttons installed on the panel of the cabinet body. Operators can directly press the start or stop buttons to control the equipment. Automatic control can be realized by connecting to an external automated control system (such as a PLC) and controlling the equipment according to preset programs and conditions.
- **Protection Function**:
- It has multiple protection functions such as overload protection, short-circuit protection, undervoltage protection, and overvoltage protection. By reasonably setting the parameters of protection components, it can ensure that electrical equipment is protected in a timely manner under various abnormal conditions. For example, setting undervoltage protection can prevent equipment from operating under the condition of too low voltage and avoid motors from being burned out due to undervoltage overload.
### IV. Application Scenarios - **Industrial Field**:
- In the production workshops of factories, the AP control cabinet is used for power distribution and control of various production equipment (such as machine tools, injection molding machines, conveyor belt motors, etc.). It can realize centralized control and management of equipment, which is convenient for maintenance and operation. For example, in an automobile manufacturing workshop, the AP control cabinet provides power support and control for welding robots, painting equipment, etc.
- **Commercial Buildings**: - It is used to control air-conditioning systems, elevators, ventilation equipment, etc. in commercial places. For example, in a large shopping mall, the AP control cabinet can distribute power to and control the compressors, fans and other equipment of the central air-conditioning system to ensure the comfortable environment in the mall and the normal operation of the equipment.
- **Data Centers**:
- It provides power distribution and protection for servers, UPS power supplies, precision air-conditioning equipment and other equipment. Since the equipment in data centers has extremely high requirements for power quality and reliability, the AP control cabinet needs to have high-precision protection functions and stable power distribution performance. For example, it can prevent servers from being damaged due to instantaneous voltage fluctuations.