what is electrical switchgear
**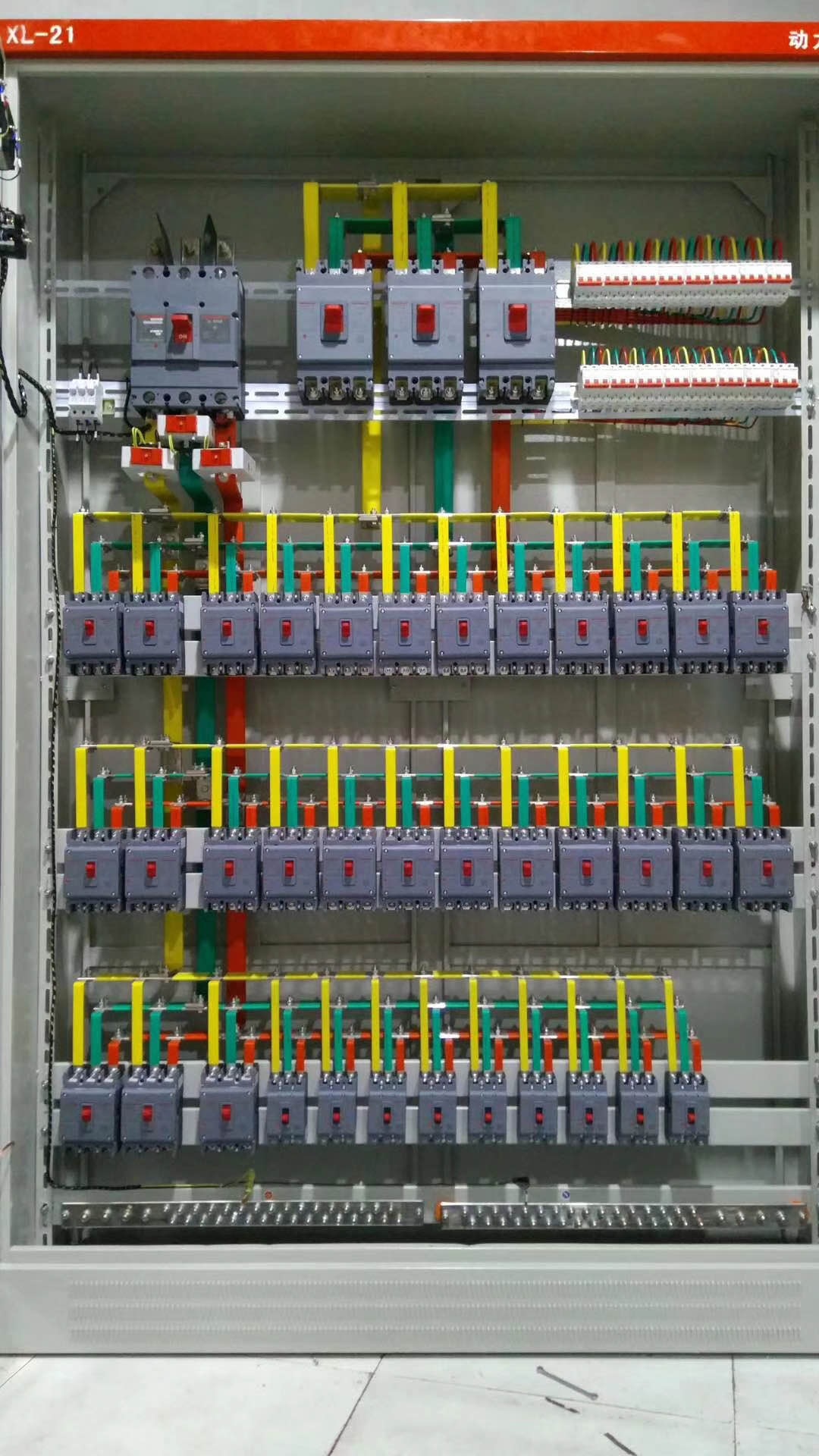
*electrical switchgear* is a core combination of equipment in electrical engineering used for **controlling, protecting, monitoring,
and managing power systems**, mainly for the safe and efficient distribution and management of electrical energy. The following
are its core definitions, functions, and technical details:
1. Definition
**Electrical switchgear** is an integrated system composed of **circuit breakers, disconnectors, fuses, instrument transformers,
relay protection devices**, etc. It is used to handle the switching on and off of electrical energy, fault protection, and status
monitoring in all links of **power generation, power transmission, power distribution, and power consumption**. It is the "nerve
center" of the power system, ensuring the safety of equipment and personnel and maintaining the stability of the power grid.
2. Core Functions
| Function | Explanation |
| Circuit Control | Manually or automatically connect/disconnect normal loads (such as starting and stopping motors), and quickly cut off the fault current in case of an emergency. |
| Fault Protection | Detect faults such as overloads, short circuits, and overvoltages, and trigger the circuit breaker to act through relay protection to avoid equipment damage. |
| Electrical Isolation | The disconnector provides a visible mechanical break to safely isolate the circuit when there is no load, facilitating maintenance. |
| Real-time Monitoring | Instrument transformers (CT/PT) convert high voltage/high current into low signals for monitoring by instruments and SCADA systems. |
| System Management | Support complex power distribution networks (such as ring networks and redundant lines), and optimize the efficiency of electrical energy distribution. |
3. Key Components
- **Circuit Breaker (CB)**
- **Function**: Actively cut off normal load current and fault current, and it can be divided into **air circuit breakers (LV)**,
**SF₆ circuit breakers (HV)**, etc.
- **Core Parameters**: Rated voltage, breaking capacity (such as a short-circuit current of 50kA).
- **Disconnector**
- **Characteristic**: It has no arc-extinguishing ability, needs to be operated in a **no-load state**, and provides a mechanical
safety break (such as the GN series disconnector).
- **Relay Protection Device**
- **Principle**: Through real-time calculation by current/voltage relays, trigger the action of the circuit breaker (such as overcurrent
protection stage I, stage II, and stage III).
- **Instrument Transformers**
- **CT (Current Transformer)**: Converts large currents into 5A or 1A (such as 1000/5A) for measurement and protection.
- **PT (Voltage Transformer)**: Converts high voltage into 100V (such as 10kV/100V) to provide voltage signals.
4. Types and Voltage Levels
| Type Type | Voltage Range | Application Scenarios | Typical Equipment |
| Low Voltage Switchgear (LV) | <1kV | Power distribution in households and commercial buildings (such as air switches, MCCB) | Power distribution boxes, Motor Control Centers (MCC) |
| Medium Voltage Switchgear (MV) | 1kV~72.5kV | Power distribution in industrial power grids and substations (such as ring main units) | Vacuum circuit breaker cabinets (such as VS1 type) |
| High Voltage Switchgear (HV) | >72.5kV | Power transmission lines and large substations (such as GIS combined electrical appliances) | SF₆ circuit breakers, GIL pipeline busbars |
5. Key Roles in Electrical Engineering
- **Power Grid Reliability**: Limit the power outage range by quickly cutting off faults (such as tripping within 10ms).
- **Energy Efficiency Management**: Smart switchgear supports **demand-side response** and optimizes power distribution
(such as in smart microgrids).
- **Safety Standards**: Comply with standards such as **IEC 62271** (high voltage) and **IEEE C37** (medium and low voltage)
to ensure insulation, temperature rise, and short-circuit withstand capacity.
Analogical Understanding
- **Household Scenario**: Similar to a power distribution box, but with **upgraded functions**: It can not only trip for protection
but also remotely monitor the current and diagnose faults (such as smart circuit breakers).
- **Industrial Scenario**: It is equivalent to the "power traffic police" of a factory, directing the flow of electrical energy in real
time and immediately "blocking the road" (isolating the fault area) in case of an accident.
Summary
Electrical switchgear is an **intelligent hub connecting the power source and the load** in electrical engineering. Through the
combination of hardware (circuit breakers, disconnectors) and software (relay protection algorithms), it realizes power control
in all scenarios from microgrids to extra-high voltage power transmission, and it is an indispensable infrastructure of modern power systems.


