The internal structure of Chint NXB series miniature circuit breakers
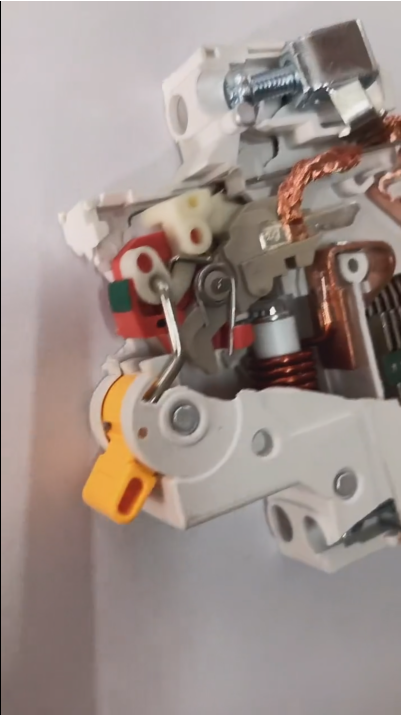 The internal structure of Chint NXB series miniature circuit breakers is based on a classic modular design, with core components including the following parts:
The internal structure of Chint NXB series miniature circuit breakers is based on a classic modular design, with core components including the following parts:
1. **Contact System and Arc Extinguishing Mechanism**
- **Contact Assembly**: Silver alloy contacts are used to ensure low-resistance conduction and anti-welding performance. The moving contact maintains contact with the static contact through a spring, and is quickly separated by the operating mechanism during opening.
- **Arc Extinguisher**: It contains 9 metal arc-extinguishing grid pieces (such as copper alloy). Using the principle that the arc is split and cooled in a magnetic field, it quickly extinguishes the arc generated by a short circuit. The arc extinguisher is made of high-temperature resistant ceramics or reinforced plastic materials to prevent arc leakage.
- **Exhaust Channel**: The high-temperature gas generated during the arc extinguishing process is discharged through the guide grooves on the top or side to avoid excessive internal pressure.
2. **Bimetallic Strip and Electromagnetic Release**
- **Overload Protection (Bimetallic Strip)**: It is made by bonding two metals with different expansion coefficients (such as copper and iron). When the current is overloaded, the bimetallic strip bends due to heat, pushing the tripping lever to trigger opening. Some models (such as NXB-63) can fine-tune the action sensitivity through an adjusting screw.
- **Short-Circuit Protection (Electromagnetic Release)**: The coil generates a strong magnetic field under a short-circuit large current, attracting the armature to hit the tripping lever. The magnetic trip threshold is usually 5-10 times the rated current (Type C) or 10-15 times (Type D), with a response time of less than 10 milliseconds.
- **Synergy Mechanism**: The bimetallic strip and the electromagnetic release share the same tripping lever to ensure the mechanical linkage of overload and short-circuit protection actions.
3. **Operating Mechanism and Energy Storage Closing**
- **Manual Operation**: The widened handle directly controls the opening and closing of the contacts through a connecting rod. Some models (such as NXB-63) adopt an "energy storage closing" design, which pre-compresses the spring through a white plastic energy storage sheet. When closing, the spring energy is released to achieve rapid closing, reducing the arc duration.
- **Automatic Tripping**: When the tripping lever is triggered, the lock releases the contact spring, the main contact is quickly disconnected under the action of the spring force, and the handle automatically bounces to the "open" position.
4. **Terminal and Insulation Design**
- **Terminal Structure**: Self-resetting screw terminals (Chint, Delixi) or self-locking terminals (Tengen) are used, supporting 2.5-10mm² copper wire connection. The terminals have no anti-misplug design, so attention should be paid to the wiring direction.
- **Insulation Material**: The shell is made of thermosetting flame-retardant plastic (such as PA66+GF30), which can withstand temperatures above 105°C. The internal live parts are isolated by insulating partitions, meeting the IP20 protection level.
5. **Modular Expansion and Safety Functions**
- **Accessory Splicing**: It supports external accessories such as auxiliary contacts, alarm contacts, and shunt releases, which can be quickly installed through rail slots. For example, the alarm contact can send a signal when the circuit breaker trips.
- **Contact Indication**: Some models (such as NXB-63) are equipped with a transparent window to display the opening and closing status of the contacts, facilitating maintenance and inspection.
6. **Pole Number Differences and Design Optimization**
- **1P/2P/3P Structure**: Arc extinguishers and releases with different pole numbers are arranged in parallel, sharing the operating mechanism. For example, a 2P circuit breaker contains two sets of contacts and arc extinguishers, with a volume twice that of 1P.
- **Magnetic Trip Optimization**: High-current models (such as NXB-125) use iron core-enhanced electromagnetic coils to increase the short-circuit breaking capacity to more than 10kA.
Technical Features and Industry Background
The Chint NXB series is imitated from the Schneider C60 platform, reducing costs through simplified design. Its arc-extinguishing grid, bimetallic strip fine-tuning and magnetic trip structures are highly similar to Schneider LS8, but the contacts adopt a square design (different from Schneider's round contacts). Compared with the early DZ47 series, NXB has added energy storage closing and contact indication functions, and the breaking capacity has been increased from 6kA to 10kA (some models).
Maintenance and Usage Suggestions
- **Installation Requirements**: Install vertically on a 35mm standard rail. The wiring screws should be tightened to the specified torque (usually 2.5N·m) to avoid virtual connection and heating.
- **Regular Inspection**: Test the tripping function every year (using special testing instruments), and check whether the arc extinguisher is carbonized and whether the terminals are loose.
- **Model Matching**: Select the trip curve according to the load type (Type C for lighting, Type D for motors), and avoid small-current models carrying high-impact loads.
Through the above design, the NXB series achieves a balance between cost and performance, and is widely used in residential and commercial power distribution systems, providing reliable overload, short-circuit protection and circuit isolation functions.


