The Principle of Voltage Regulation of Dry-Type Transformers
The principle of voltage regulation of dry-type transformers mainly realizes voltage adjustment by changing the turn ratio of the windings. The following are its core mechanisms and common methods:
I. Basic Principles of Voltage Regulation
1. **Electromagnetic Induction Law**
According to the formula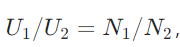 , the output voltage \(U_2\) is changed by adjusting the number of turns of the primary side (\(N_1\)) or the secondary side (\(N_2\)).
, the output voltage \(U_2\) is changed by adjusting the number of turns of the primary side (\(N_1\)) or the secondary side (\(N_2\)).
2. **Function of the Tap Changer**
Multiple taps (tap points) are set on the winding. By switching the position of the taps, the effective number of turns is changed, thus adjusting the voltage.
II. Voltage Regulation Methods
1. Off-Load Tap Changer (OLTC)
- **Operating Conditions**: Manual operation is required after power is cut off.
- **Principle**: By rotating the tap changer, different tap positions are selected to change the turn ratio of the winding.
- **Characteristics**:
- Simple structure and low cost.
- The voltage regulation range is relatively small (usually ±5% or ±2×2.5%).
- Suitable for occasions with small voltage fluctuations (such as residential power distribution).
2. On-Load Tap Changer (OLTC)
- **Operating Conditions**: It can be adjusted automatically or manually with a load.
- **Principle**:
- The circulating current during tap switching is limited by the transition resistance to achieve smooth voltage regulation.
- The microprocessor or controller monitors the voltage in real time and automatically adjusts the taps.
- **Characteristics**:
- A large voltage regulation range (up to more than ±10%).
- Fast response speed, suitable for industrial scenarios with severe voltage fluctuations (such as steel plants, data centers).
- Higher cost and requires regular maintenance.
III. Typical Voltage Regulation Processes
1. **Steps of Off-Load Voltage Regulation**
- Cut off the power → Open the tap changer cover → Rotate the handle to the target gear → Reset and lock → Close the switch for testing.
2. **Process of On-Load Voltage Regulation**
- The controller detects the voltage deviation → The driving motor rotates the tap changer → The transition resistance is connected for a short time → The tap switching is completed → Return to normal operation.
IV. Key Design Points
1. **Types of Tap Changers**
- **Manual Type**: Used for off-load voltage regulation and requires manual operation.
- **Electric Type**: Used for on-load voltage regulation and supports remote control.
2. **Winding Structure**
- Tap points are set on the high-voltage winding (because the current on the high-voltage side is small, and the risk of arcing during switching is low).
- The tap points are usually located in the middle of the winding to balance the voltage regulation range.
3. **Insulation and Heat Dissipation**
- The tap changer needs to have a high insulation grade to avoid creepage or short circuit.
- The air-cooling or self-cooling design of the dry-type transformer needs to ensure good heat dissipation of the voltage regulation components.
V. Application Scenarios
- **Off-Load Voltage Regulation**: Suitable for scenarios with stable voltage and small load changes (such as community power distribution, small factories).
- **On-Load Voltage Regulation**: Suitable for scenarios with large voltage fluctuations and the need for real-time adjustment (such as power substations, power supply for precision manufacturing equipment).
VI. Precautions
1. **Safe Operation**
- Off-load voltage regulation must be operated with the power cut off to avoid electric shock or equipment damage.
- For on-load voltage regulation, the transition resistance and the wear condition of the contacts need to be checked regularly.
2. **Maintenance Suggestions**
- Check the contact pressure of the tap changer contacts every 1 to 2 years (it needs to be maintained at 150~200N).
- Clean the dust inside the tap changer to prevent the insulation from decreasing.
If you need the voltage regulation parameters or operation guidelines of specific models, you can provide the information on the transformer nameplate (such as capacity, voltage level), and I will provide further answers.


