What size of air switch and electrical wire are needed for a total household electrical power of 8KW
According to the household electrical standards in Los Angeles County, California, the United States (120/240V single-phase system), the power distribution scheme for a total household power of 8kW is as follows:
### 1. Selection of Air Switch (Circuit Breaker)
- **Calculation of Total Current**:
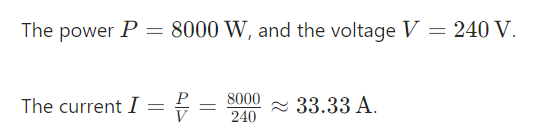
- **Specification of the Circuit Breaker**:
Select a **40A double-pole circuit breaker** (which complies with the NEC standard and has a rated current slightly larger than the calculated value).
### 2. Selection of Electrical Wire Specification
- **Requirement for Current-carrying Capacity**:
For a current of \(33.33 \, \text{A}\), an **8 AWG copper-core electrical wire** should be used (with a safe current-carrying capacity of **40A**, meeting the NEC insulation requirement at 60℃).
(If the length of the circuit exceeds **50 feet**, it is recommended to upgrade to **6 AWG** to reduce the voltage drop.)
YouTube:https://youtube.com/shorts/NMjL05pxT-w
- **Type of Electrical Wire**:
It is recommended to use **THHN/THWN-2** insulated copper wire (suitable for dry indoor environments).
3. Installation Precautions
1. **Type of Circuit Breaker**:
Use a **double-pole circuit breaker** (for 240V power supply), instead of a single-pole one (120V).
2. **Circuit Protection**:
Ensure that the electrical wire is protected by being threaded through a pipe (such as an EMT galvanized steel pipe or a PVC conduit).
3. **Voltage Drop**:
If the circuit is long (more than 100 feet), the voltage drop needs to be recalculated and the wire diameter adjusted.
4. **Compliance**:
Comply with local electrical codes (such as the California Electrical Code CEC) and have the installation carried out by a licensed electrician.
Summary
- **Circuit Breaker**: 40A double-pole circuit breaker
- **Electrical Wire**: 8 AWG THHN/THWN-2 copper-core wire
- **Suggestion**:
If the household load is likely to increase (such as planning to install an air conditioner or an electric vehicle charging pile), reserve space for upgrading (such as selecting a 6 AWG electrical wire + a 50A circuit breaker).
🔌 Safety Tips:
- Avoid overloading operation and regularly check the aging condition of the circuit.
- If you are not sure about the specific configuration, it is recommended to contact a professional electrician for on-site evaluation.
What is an Arc Flash?
- **Definition**: When a phase-to-phase or phase-to-ground short circuit occurs inside high-voltage or low-voltage electrical equipment (such as switchgear and circuit breakers), the current ionizes through the air to form a high-temperature and high-energy electric arc, releasing intense light, shock waves and extremely high temperatures (which can reach tens of thousands of degrees Celsius).
- **Characteristics**:
- It releases a huge amount of energy instantaneously, which may trigger fires, explosions or equipment melting.
- The intense light (arc light) generated may cause blindness, and the high-temperature radiation may cause serious burns.
Common Causes of Arc Flashes
1. **Equipment Aging or Damage**: Insulation material failure, loose contacts, dust accumulation, etc.
2. **Operation Errors**: Misoperation of circuit breakers, maintenance without power cut-off, use of unqualified tools.
3. **Environmental Factors**: Moisture, corrosive gases, intrusion of small animals.
4. **Design Flaws**: Insufficient protection level, poor heat dissipation, short-circuit capacity exceeding the equipment's bearing capacity.
Hazards of Arc Flashes
- **Personal Injuries**: Burns, hearing damage, blindness, internal organ damage (caused by shock waves).
- **Equipment Damage**: Switchgear burning, busbar fusing, control system paralysis.
- **Economic Impact**: Long-term power outages, high maintenance costs, production interruptions.
Measures to Prevent Arc Flashes
1. **Equipment Design and Maintenance**:
- Select arc flash protection switchgear that meets the standards (such as IEEE C37.20.7).
- Regularly check the insulation performance, clean the equipment, and replace aging components.
- Install arc flash protection devices (such as arc sensors + fast circuit breakers) to quickly cut off the fault current.
2. **Safe Operation Specifications**:
- Strictly implement the power cut-off, voltage testing and grounding procedures, and use insulated tools.
- Carry out "live-free operation" on high-risk equipment or adopt remote monitoring.
- Restrict unauthorized personnel from entering the power distribution area.
3. **Risk Assessment and Training**:
- Determine the risk level through **Arc Flash Hazard Analysis**.
- Provide professional training for employees to ensure they are familiar with the emergency response plan and the use of protective equipment.
4. **Physical Protection**:
- Use **Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)**: Arc-resistant suits, face masks, gloves, insulated shoes, etc.
- Set up protective barriers or warning signs around the switchgear.
Relevant Standards and Regulations
- **American Standards**:
- NFPA 70E (Electrical Safety Standard) specifies the arc flash risk assessment and PPE requirements.
- OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) requires employers to provide a safe working environment.
- **International Standard**: IEC 61641 (Arc Flash Protection for Low-Voltage Switchgear).
Emergency Response Procedures
1. **Cut off the Power Supply Immediately**: Use the emergency trip device or remote operation to disconnect the faulty circuit.
2. **Evacuate Personnel**: Stay away from the arc area to avoid secondary injuries.
3. **Fire Fighting and Rescue**: Use dry powder fire extinguishers to put out the fire, and give priority to treating the injured.
4. **Accident Investigation**: Analyze the cause, improve the protection measures, and prevent recurrence.
If you need more specific technical details (such as arc flash energy calculation, selection of protective equipment) or case analysis, please feel free to let us know! 🔋🚒


