10kV high-voltage outgoing cabinet
Product description
 I. Definition
I. Definition
1. **Basic concept**
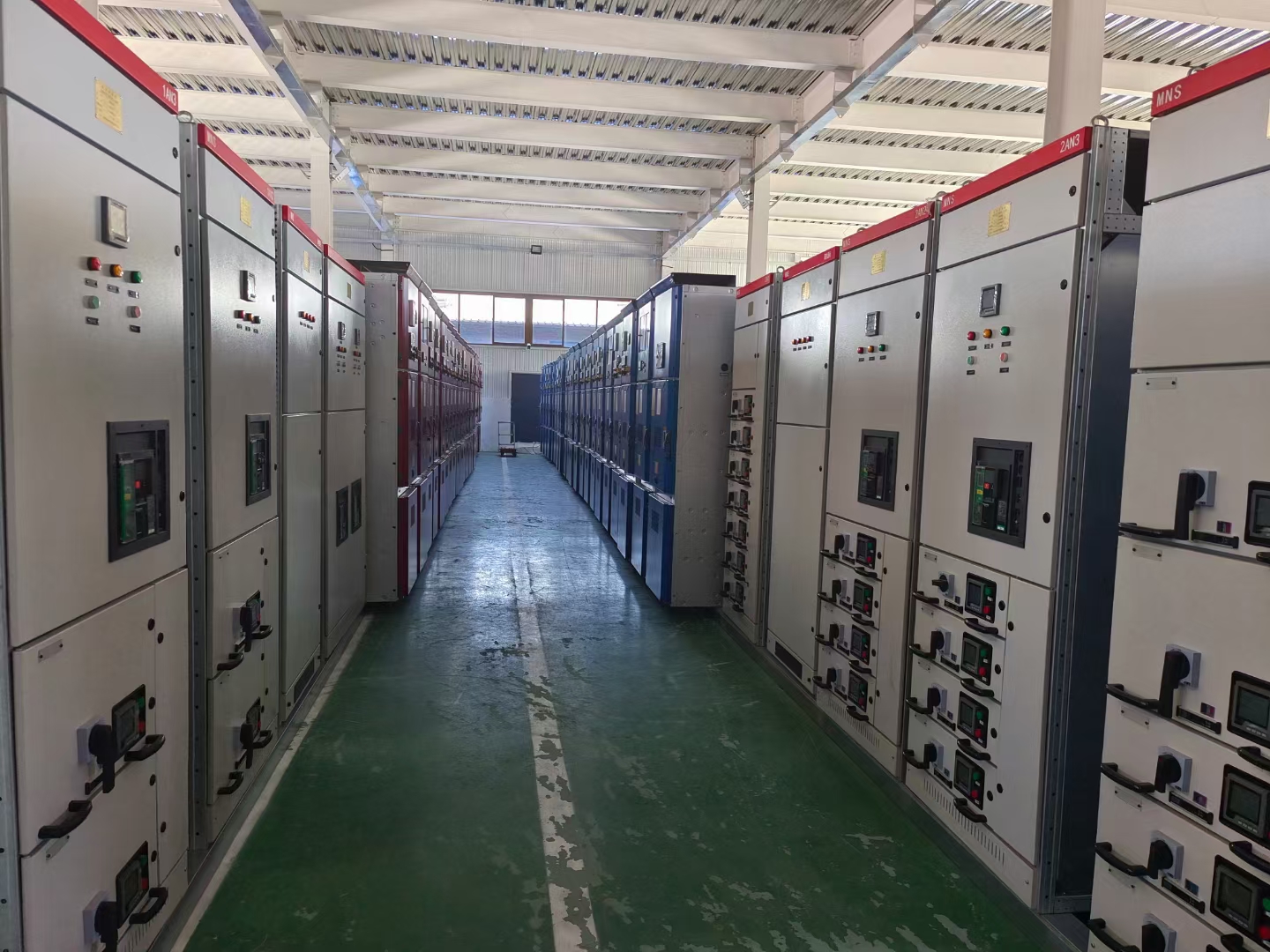
- The 10kV high-voltage outgoing cabinet is an important cabinet in the power distribution device of the 10kV voltage level. It is mainly used to distribute the electric energy on the 10kV bus to different outgoing circuits and is a key equipment connecting the bus and external power lines (such as transmission lines, subordinate substations or user ends, etc.).
II. Structural composition
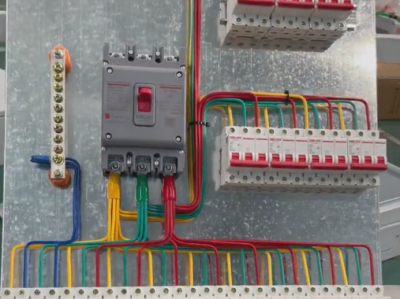
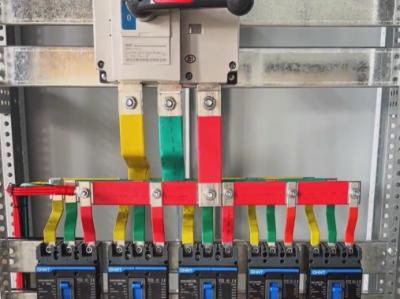
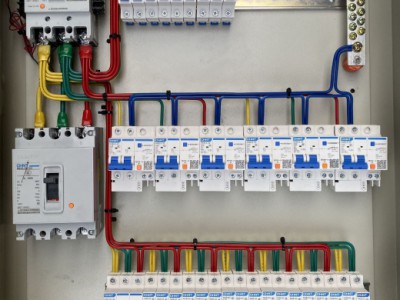
1. **Cabinet body**
- The cabinet body provides basic physical protection and installation space for the outgoing cabinet. Generally made of metal materials, it has good grounding performance to ensure the safety of equipment and personnel. The cabinet structure is solid and can withstand certain mechanical stress. It also has good sealing performance to prevent dust, moisture, etc. from entering the cabinet and affecting the normal operation of the equipment.
2. **Circuit breaker**
- The circuit breaker is one of the core components of the 10kV high-voltage outgoing cabinet. It can cut off the circuit under normal and fault conditions and has strong arc extinguishing ability. When faults such as overload and short circuit occur, the circuit breaker can act quickly to disconnect the faulty circuit and protect the safety of equipment and lines. Common 10kV circuit breakers include vacuum circuit breakers and other types. They have high working reliability and relatively small maintenance.
3. **Disconnecting switch**
- The disconnecting switch is mainly used to isolate the circuit when there is no current, providing an obvious disconnection point for the convenience of equipment inspection and maintenance. When performing inspection work on the outgoing cabinet, first disconnect the circuit breaker and then pull open the disconnecting switch to ensure the safety of inspection personnel. The operation of the disconnecting switch must be carried out in strict accordance with operating procedures to prevent dangerous operations such as pulling the switch under load.
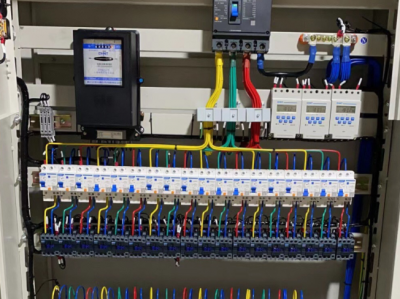
4. **Current transformer**
- The current transformer is used to measure the current magnitude in the outgoing circuit. It transforms the large current into a small current in proportion (generally the standard secondary current, such as 5A or 1A), so that measuring instruments (such as ammeters) and protection devices (such as relay protection devices) can perform current measurement and fault judgment. The secondary side of the current transformer is strictly prohibited from being open-circuited, otherwise high voltage will be generated, endangering the safety of equipment and personnel.
5. **Voltage transformer**
- The voltage transformer is used to measure the voltage of the outgoing circuit. It transforms the high voltage into a low voltage in proportion (generally the standard secondary voltage, such as 100V), providing voltage signals for measuring instruments such as voltmeters and electric energy meters and voltage protection devices. The secondary side of the voltage transformer is strictly prohibited from being short-circuited, otherwise the transformer will be damaged.
6. **Relay protection device**
- The relay protection device is an important part of the 10kV high-voltage outgoing cabinet. It monitors the electrical parameters (such as current, voltage, power, etc.) in the circuit in real time. When faults or abnormal conditions (such as overcurrent, overvoltage, undervoltage, etc.) are detected, it can quickly send out signals to trip the circuit breaker, cut off the faulty circuit, and protect the equipment and lines from further damage. Common types of relay protection include overcurrent protection, instantaneous trip protection, zero sequence protection, etc.
7. **Earthing switch**
- The earthing switch is used to ground the line side of the outgoing cabinet during inspection to ensure the safety of inspection personnel. Before performing inspection operations, the earthing switch must be closed first to reliably ground the potentially live parts to prevent electric shock accidents caused by sudden power supply.
III. Working principle
1. **During normal operation**
- Under normal operating conditions, the circuit breaker is in the closed state. The current flows through devices such as circuit breakers and disconnecting switches to the outgoing circuit and transmits the electric energy on the 10kV bus to the external line. The current transformer and voltage transformer monitor the current and voltage parameters in the circuit in real time and transmit signals to measuring instruments and relay protection devices for electric energy metering and operation status monitoring.
2. **In case of fault**
- When a fault occurs in the outgoing circuit, such as a short circuit or overload, the relay protection device will quickly detect the fault according to the set protection action value. For example, in overcurrent protection, if the current exceeds the set overcurrent protection value, the relay protection device will send a trip signal to the circuit breaker. After receiving the signal, the circuit breaker quickly disconnects the circuit to isolate the faulty part and prevent the expansion of the fault range. At the same time, the earthing switch plays a role in grounding protection during inspection to ensure inspection safety.
IV. Application scenarios
1. **Substation**
- In a substation, the 10kV high-voltage outgoing cabinet is a key equipment for distributing the electric energy of the 10kV bus of the substation to various outgoing directions. It can transmit electric energy to different power consumption areas such as subordinate substations, factories, and residential areas to realize the reasonable distribution and transmission of electric energy.
2. **Industrial enterprises**
- For the 10kV power distribution system inside industrial enterprises, the high-voltage outgoing cabinet distributes the electric energy of the 10kV bus of the enterprise's total step-down substation to the power supply lines of various workshops, branches or large equipment to meet the power needs of different electrical equipment inside the enterprise.